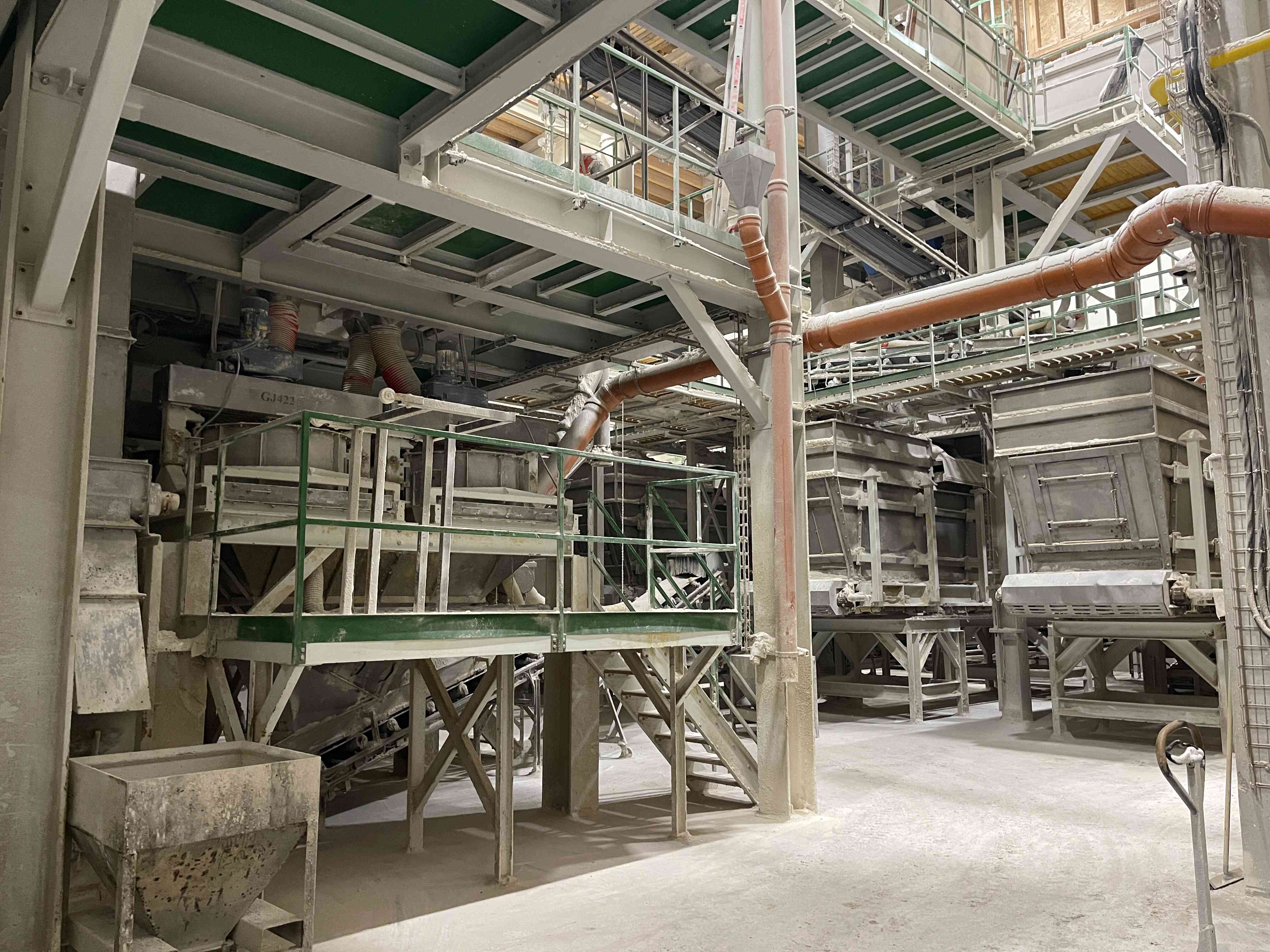
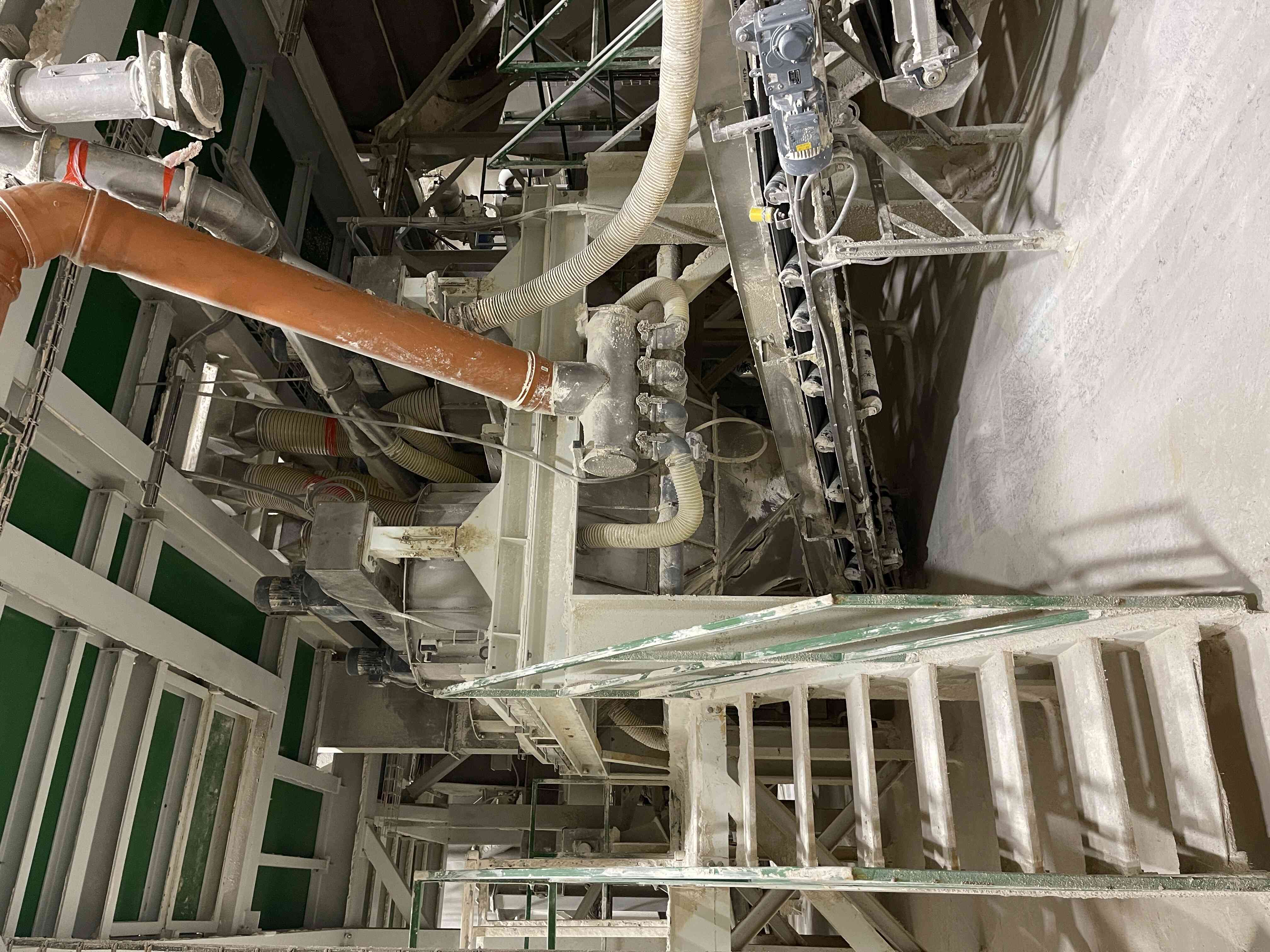
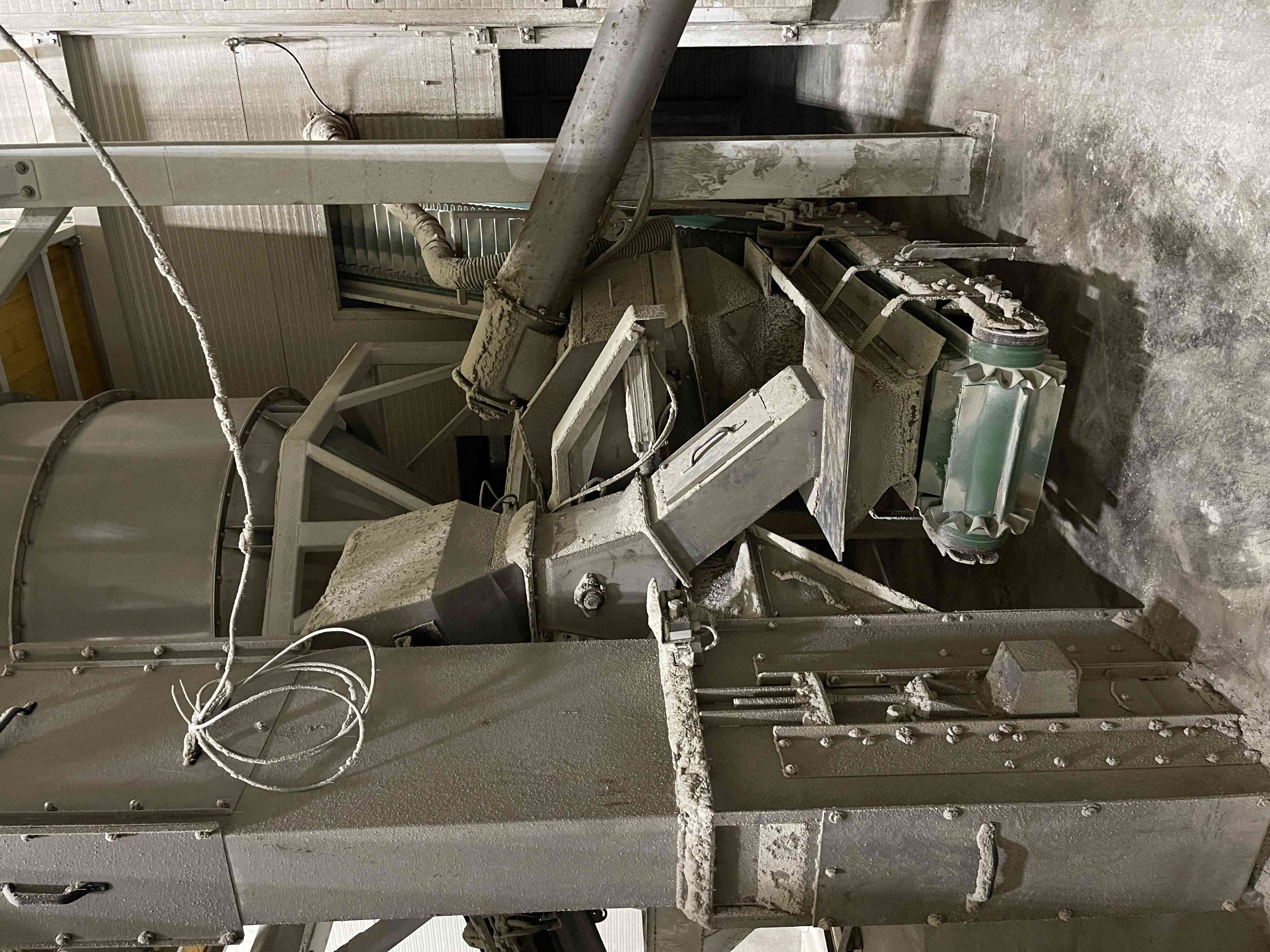
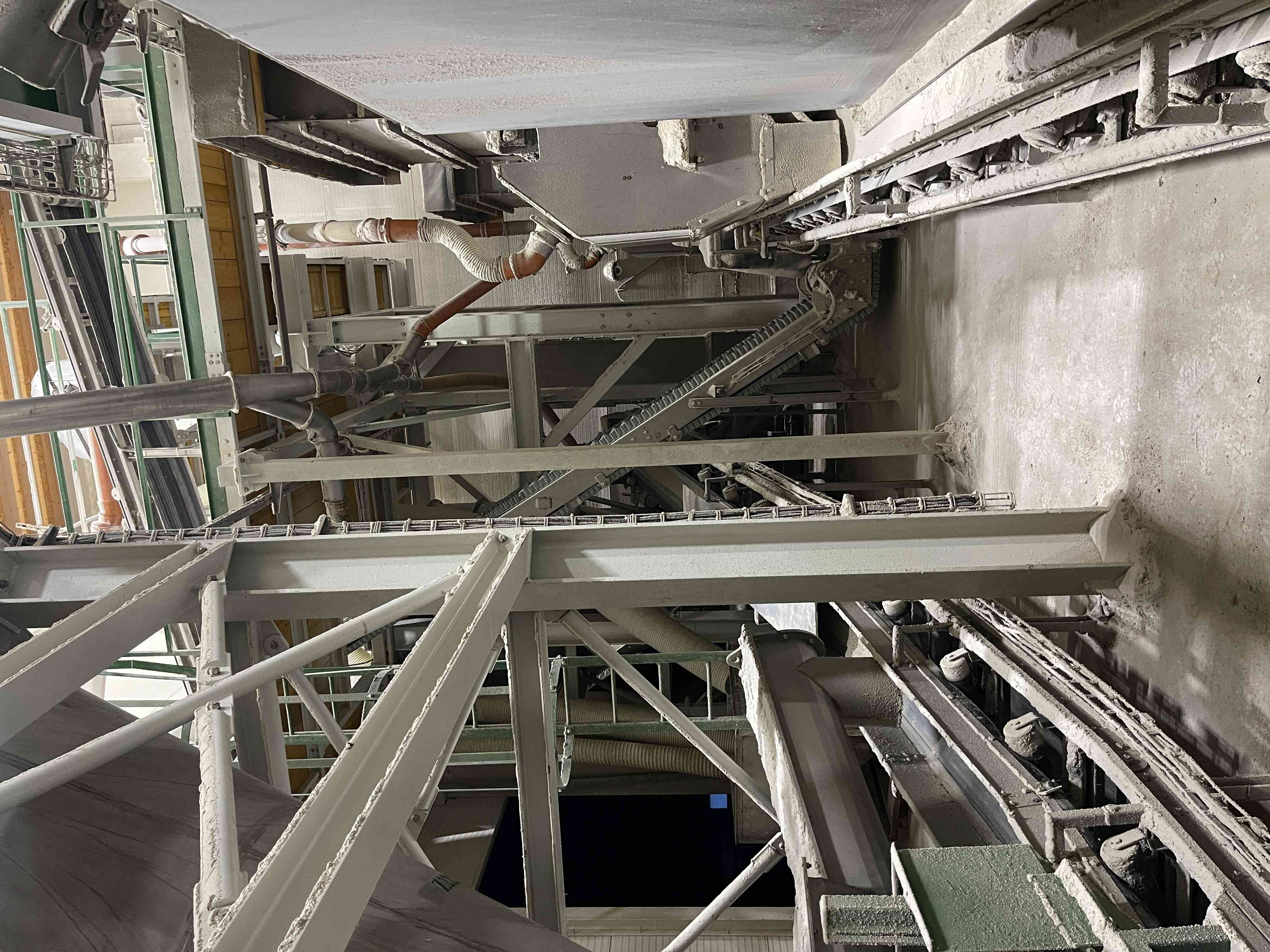
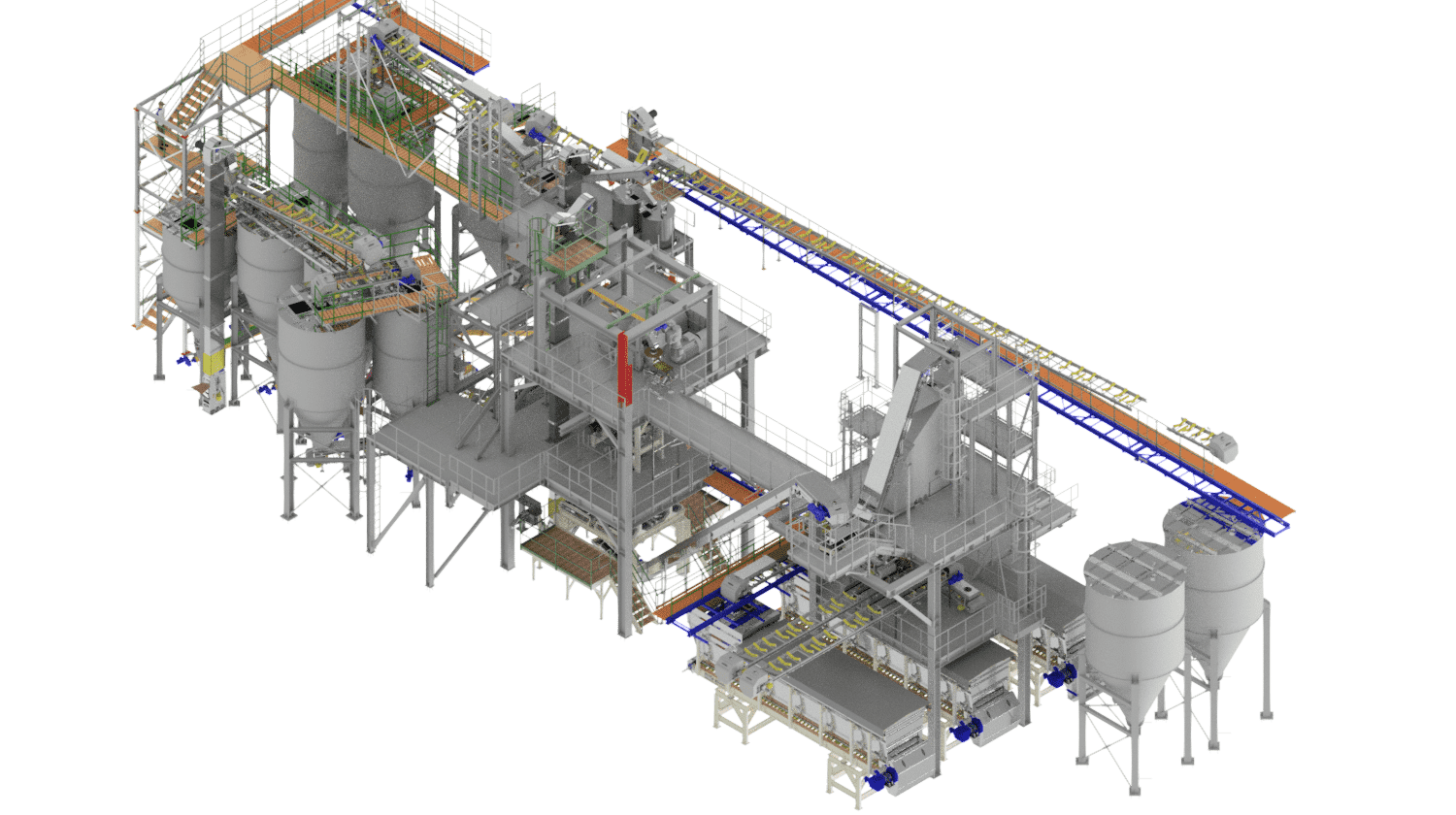
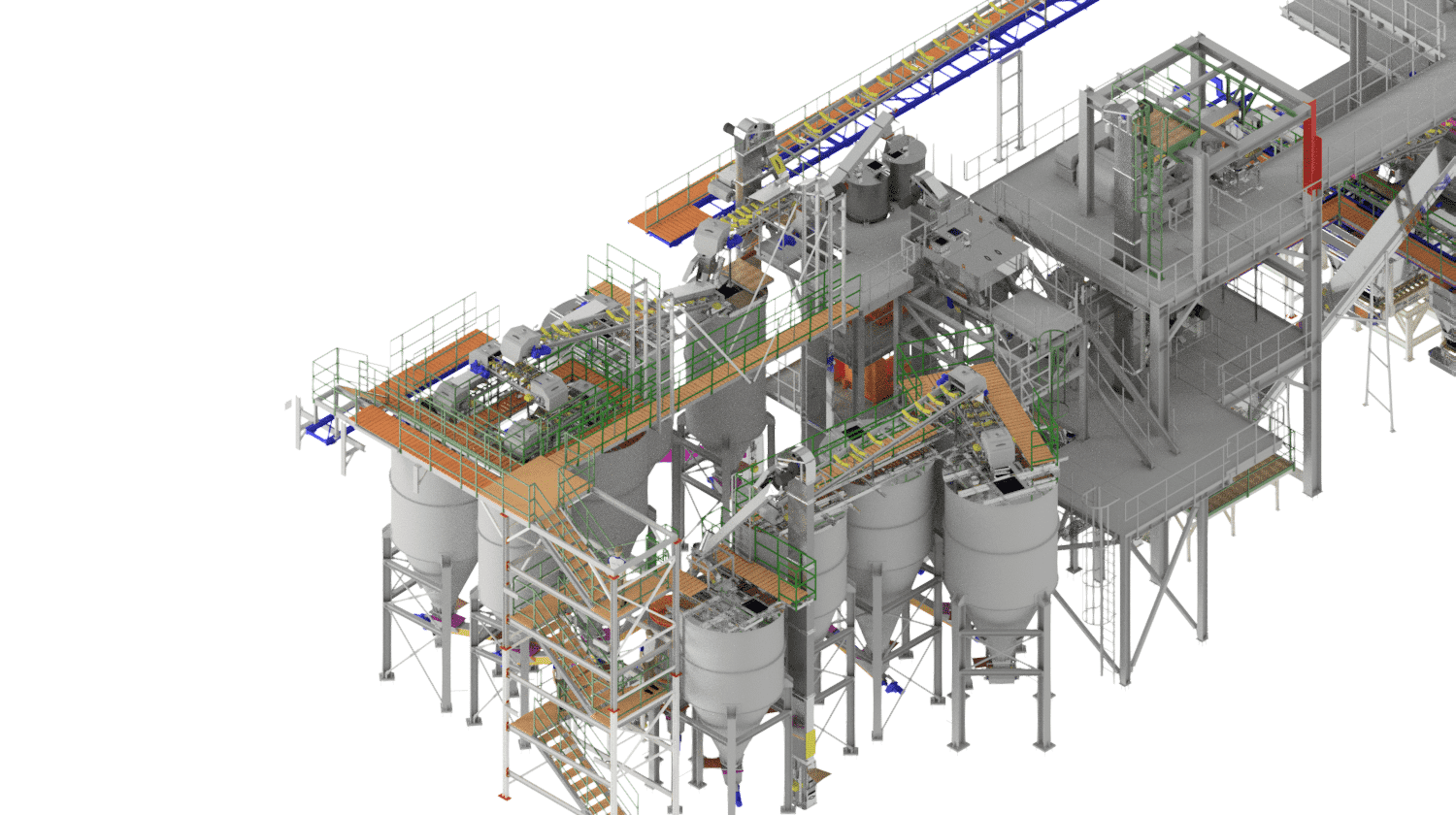
Compaction is the process of producing fully-fledged industrial fertilizer granules from single-component substances using a dry method. Each granule contains a set ratio of input raw materials, i.e., nutrients, according to the chosen formula. It is a highly efficient technology where, under high pressure, a continuous compressed sheet is formed from a mixture of input materials, which is then disintegrated into individual granules. This is a closed, waste-free process of completely converting input materials into the final product.
The line allows high variability of formulations, fertilizer compositions, and quick changes in production assortments.
The performance of compaction lines depends on customer requirements, to which the size of individual line devices is adapted.
The compaction process consists of 8 sub-processes:
- Storage bins for input raw materials with weighted outputs to ensure the correct mix ratio
- Grinding of input raw materials
- Mixing of the blend
- Compaction of the mixture with subsequent granulation
- Sorting of the compacted material
- Air handling system
- Product maturation
- Granule surface treatment
1. Storage bins for input raw materials
The bins are designed based on the number of input raw materials, usually consisting of input hoppers with a capacity of 5 m³ to 8 m³ with raw material feeders or silos with feeders for fine materials. The bins are filled using a front loader. The system weighs individual raw materials into weighted intermediate bins based on the formula, from which the material is fed onto transport paths leading to the mixing process. This is a batch process.
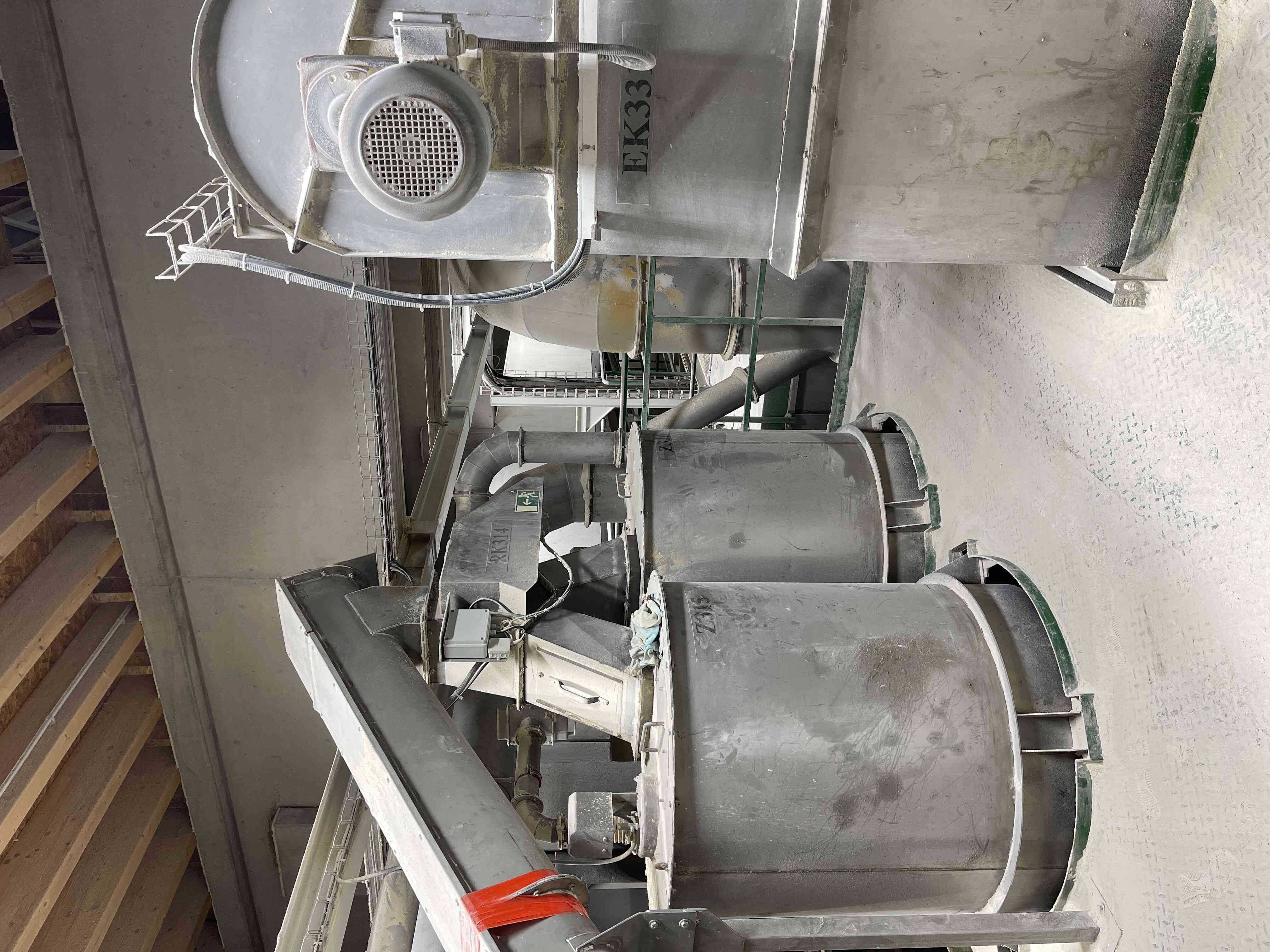
2. Raw material grinding process
Some coarse raw materials need to be ground into finer fractions before entering the compaction process. The input material is fed in batches from the input bin into an intermediate bin before the mill to ensure the proper composition of the prepared component, and from there it is continuously dosed into the pin mill, where it is ground to the required fraction. For safety and mill protection, a detector for metallic and non-metallic particles is installed before the mill. The ground input material can be fed into an output bin or a container.
3. Mixing of the blend
The dosed blend is fed into a batch mixing device where the raw materials are thoroughly mixed, and trace elements may be added using vibrating weighted feeders or a specific amount of granulation liquid. Paddle mixers are used for mixing. After mixing, the blend is directed to an intermediate bin before the compactor.
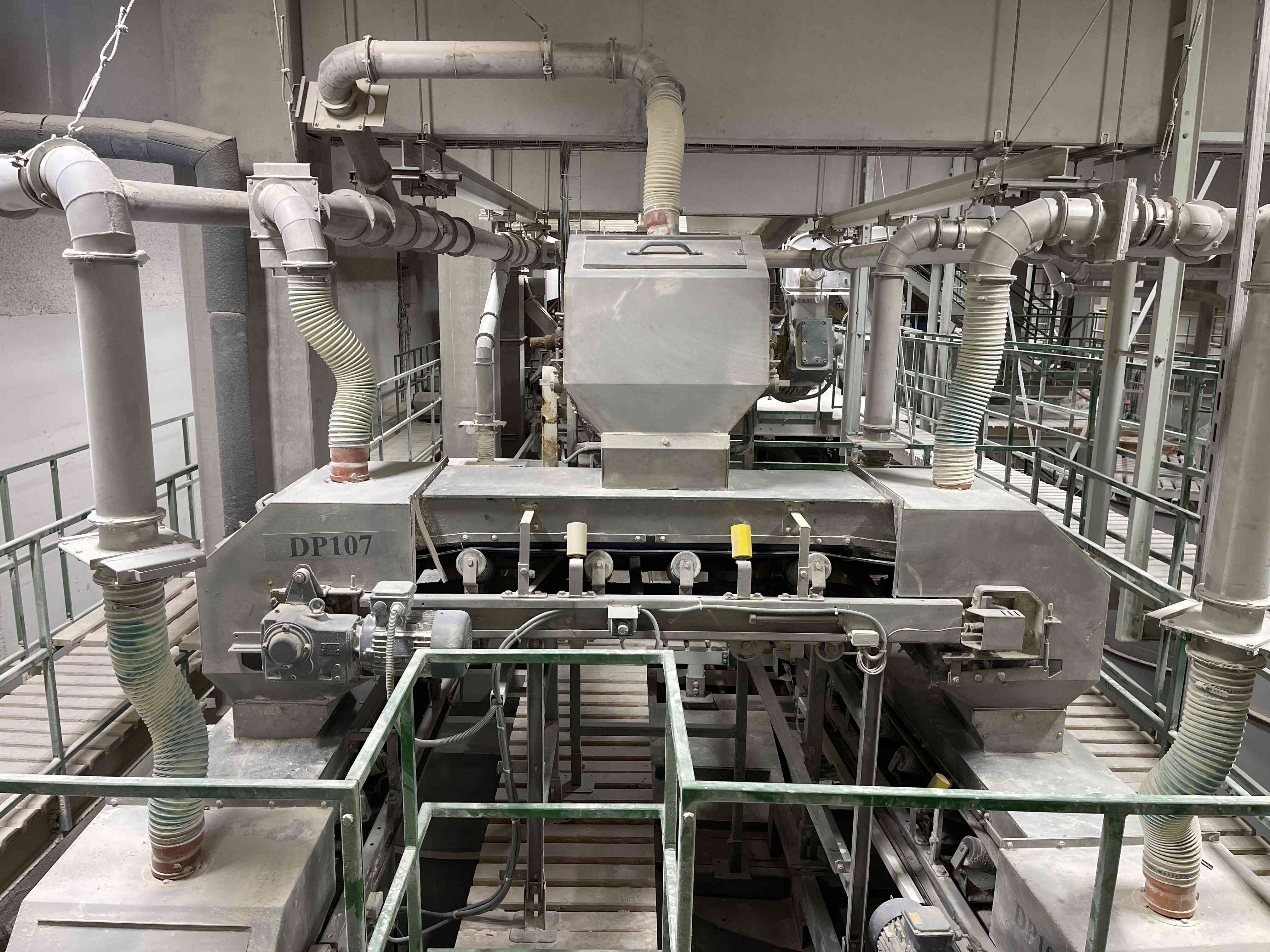
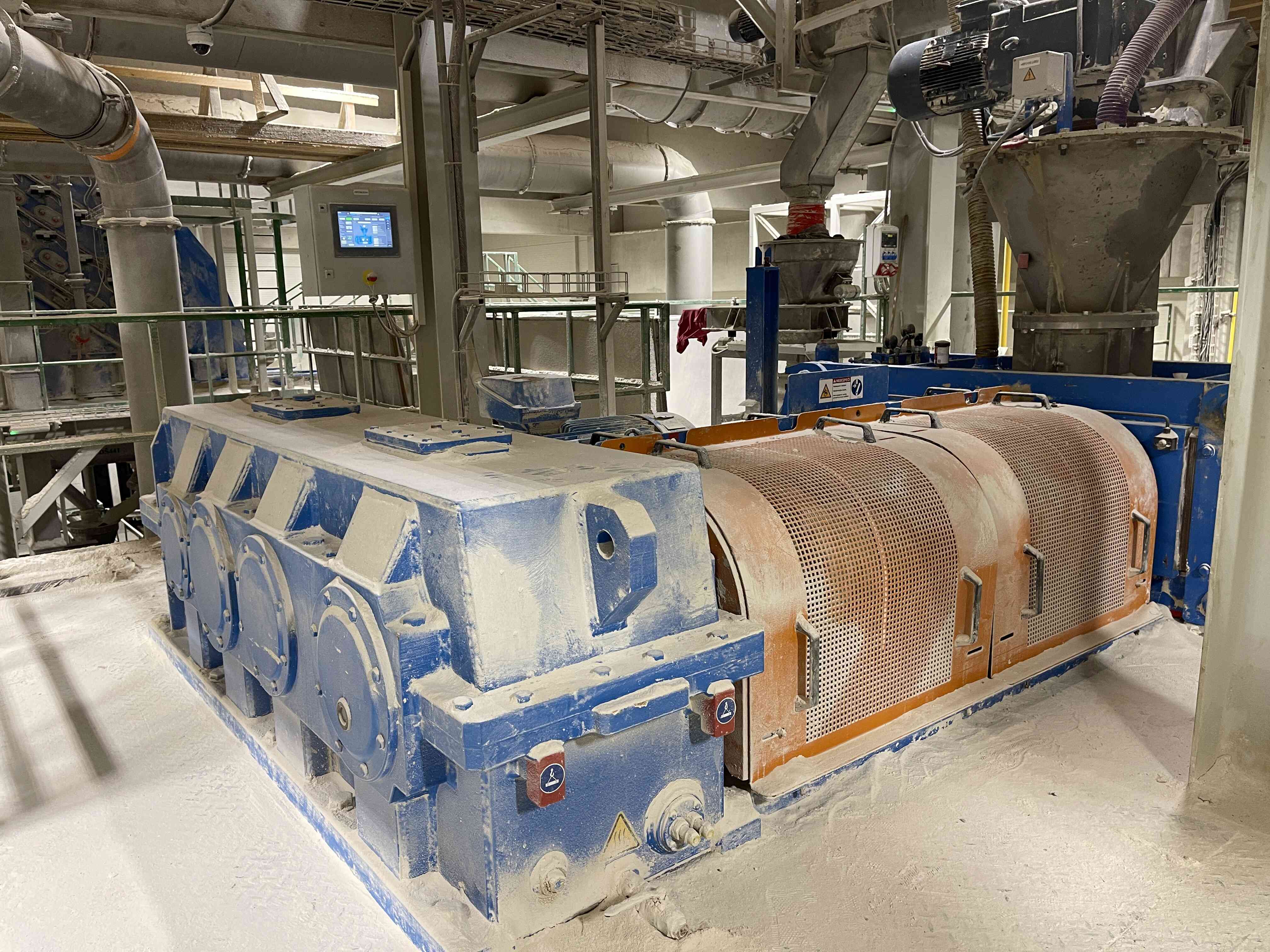
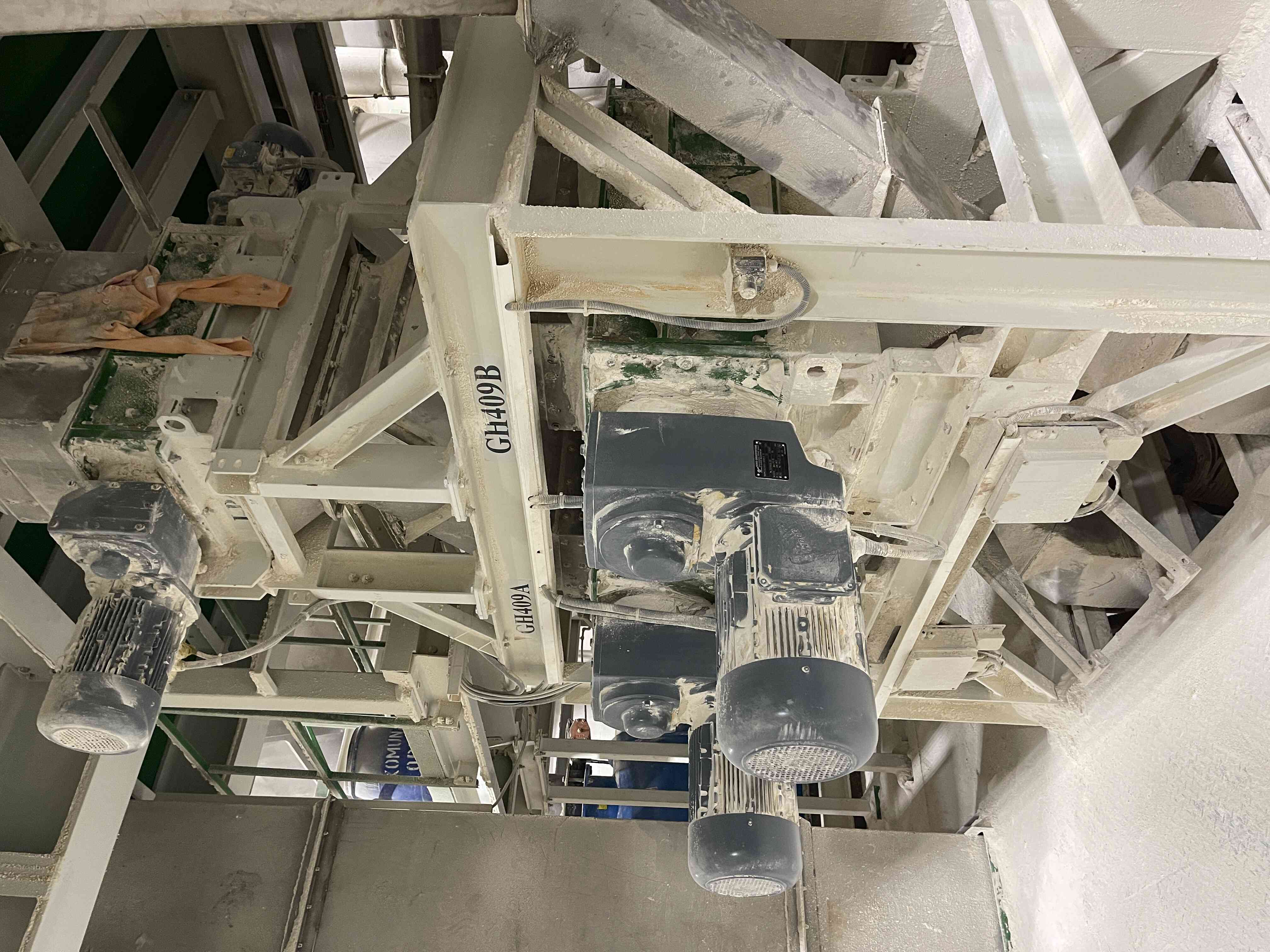
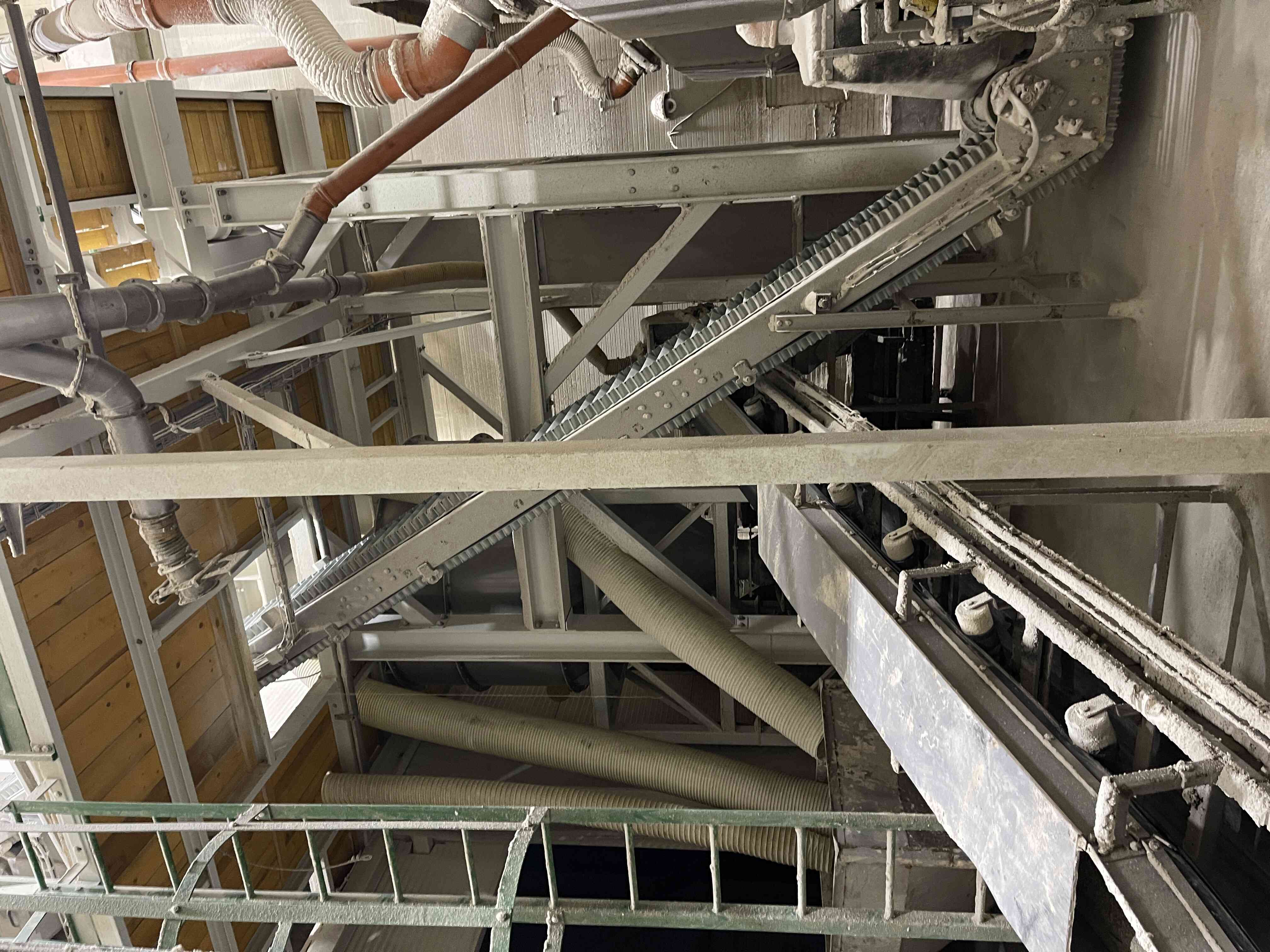
4. Compaction of the mixture with subsequent granulation
The mixed raw material and return material (recycle) are dosed here in precisely determined ratios and transported to the compactor's input hopper. The compactor presses a sheet of approximately 8 to 10 mm thickness from the input raw materials, depending on the process requirements. This sheet is then carefully disintegrated into granules (sheet breaker, horizontal granulators, and vertical granulators). The disintegrated material is subsequently sent to the sorting section.
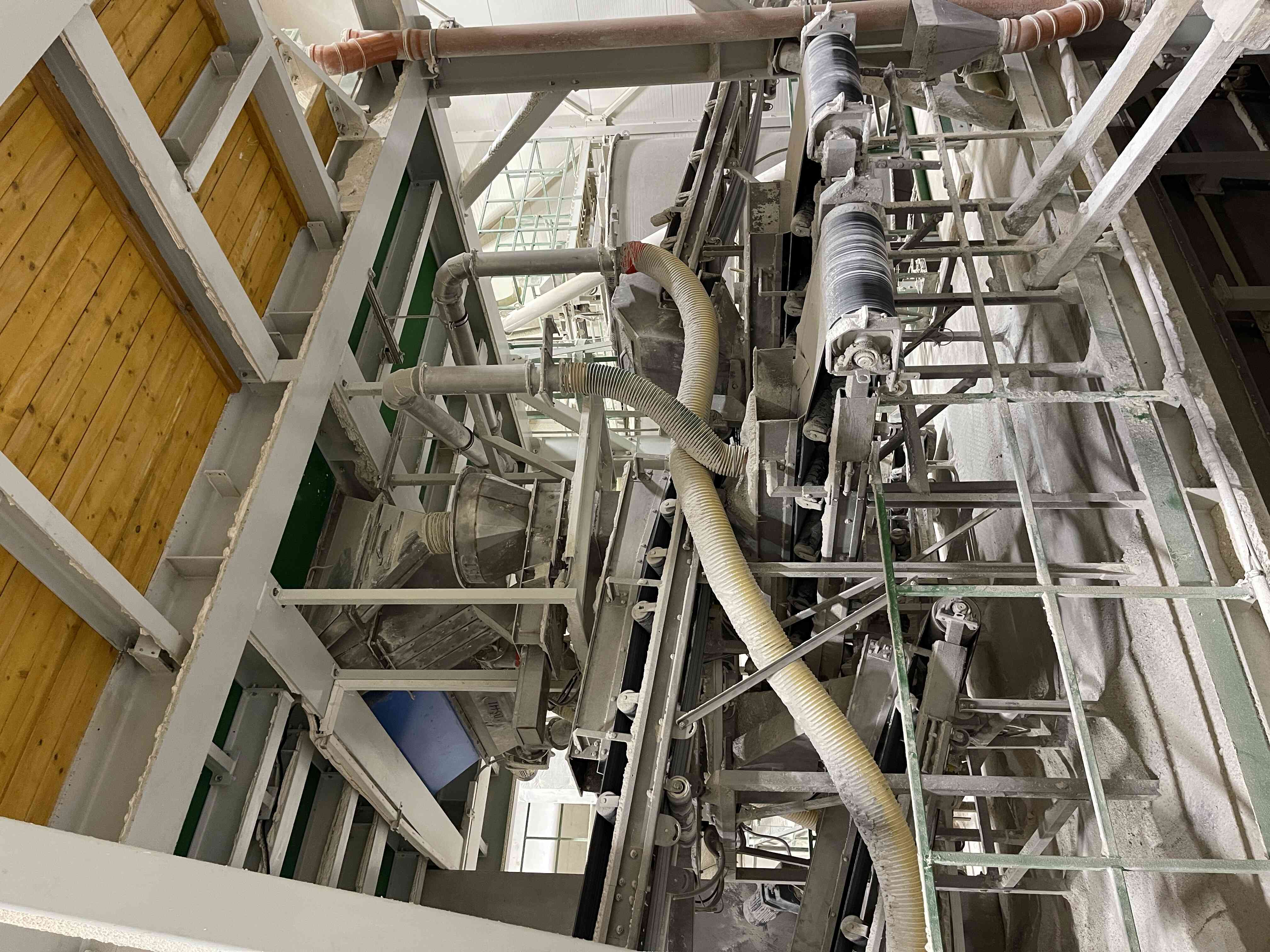
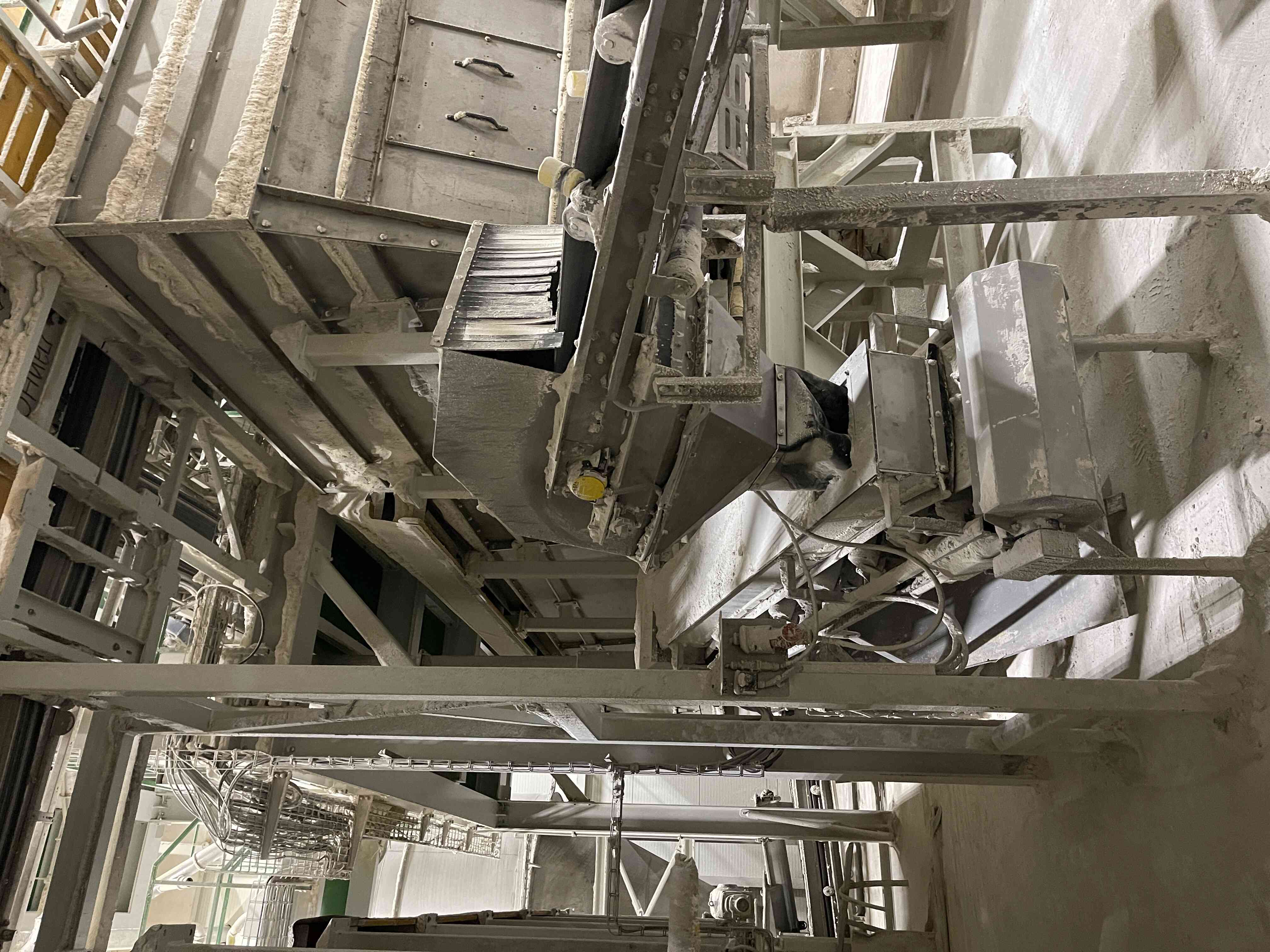
5. Sorting of the compacted material
The disintegrated material enters the input of a vibrating sorter where it is sorted into desired granule sizes based on the mesh sizes installed in the sorter. The oversized material (coarse recycle) is returned to the compaction process and disintegrated into granules. The product fraction is transported to maturation bins, and the undersized material (fine recycle) is returned to the input before the compactor, where it is dosed into fresh material.
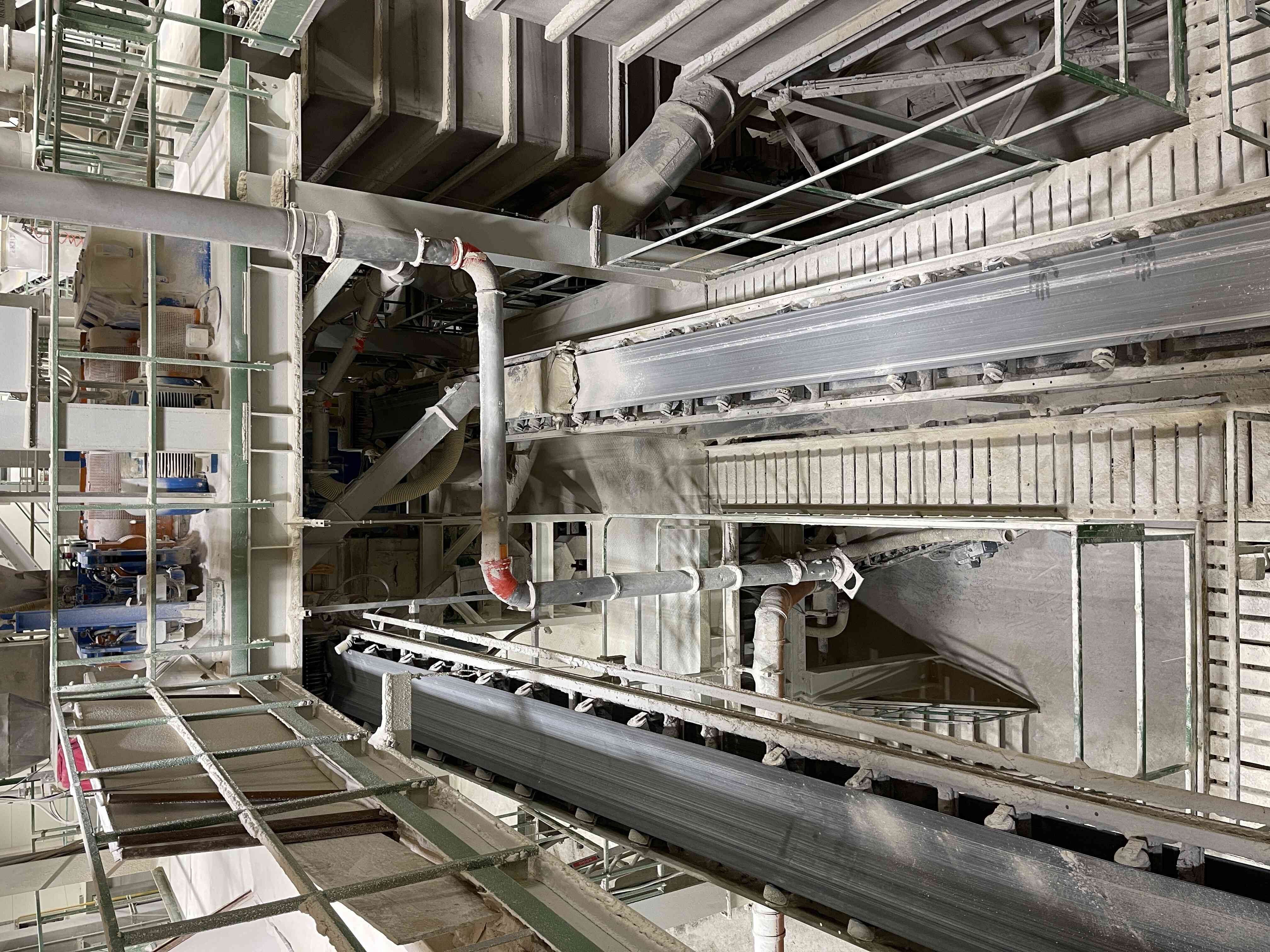
6. Air handling system
An essential part of a well-functioning compaction process is the maximum dust removal from the entire process, where all exposed points are under vacuum and exhausted. The extracted dust is returned to the process.
7. Product maturation
Product maturation takes place either in maturation bins where the product is stored for a specified period to allow granules to mature and complete the compaction process, or through cooling of granules after compaction and before entering maturation bins.
8. Granule surface treatment
Granule surface treatment is carried out after the maturation process and before the compaction product is dispatched, either by spraying with oil or wax to reduce granule stickiness during further storage or by spraying with dye if color adjustment of the granules is required. Dust separation should ideally be repeated in this process.